Imagine waking up to the smell of freshly brewed coffee, your thermostat adjusting to the perfect temperature, and your smartwatch gently nudging you awake all without lifting a finger. This seamless automation is made possible by the Internet of Things (IoT), a rapidly growing technology that connects everyday objects to the internet, transforming the way we live and work.
In today’s digital world, IoT is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a reality shaping our daily lives. From smart homes to connected health devices, IoT offers unmatched convenience and efficiency. However, with this connectivity comes concerns about data security, privacy, and reliability.
In this article, we’ll explore what IoT is, how it works, and how it impacts our daily routines. You’ll gain valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and future trends of IoT, helping you navigate this ever-evolving technology with confidence.
What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical objects devices, appliances, and even vehicles that are connected to the internet and can collect, share, and analyze data. These devices are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity features that allow them to interact with each other and with users, making everyday tasks smarter and more efficient.
Core Components of IoT
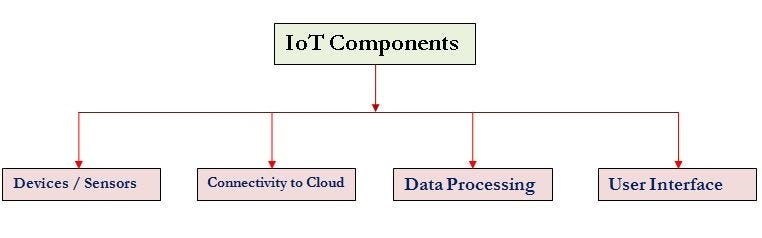
To better understand IoT, let’s break down its key components:
- Sensors and Devices:
- These are the “eyes and ears” of IoT. Sensors collect data such as temperature, movement, light, or humidity from the environment. Examples include smart thermostats that measure room temperature or fitness trackers that monitor heart rates.
- Connectivity:
- Once data is collected, devices use communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks to transmit the information to cloud-based systems for processing. Without connectivity, IoT devices cannot function effectively.
- Data Processing:
- The gathered data is processed either locally (on the device) or in the cloud to generate insights or trigger automated actions. For instance, a smart security camera can detect movement and send alerts to your phone.
- User Interface:
- Users interact with IoT devices through mobile apps, web dashboards, or voice assistants, making it easy to control and monitor devices remotely. Smart speakers like Alexa or Google Home are prime examples of this interaction.
IoT simplifies life by connecting these elements to provide seamless automation, improve decision-making, and create personalized experiences.
How IoT Works
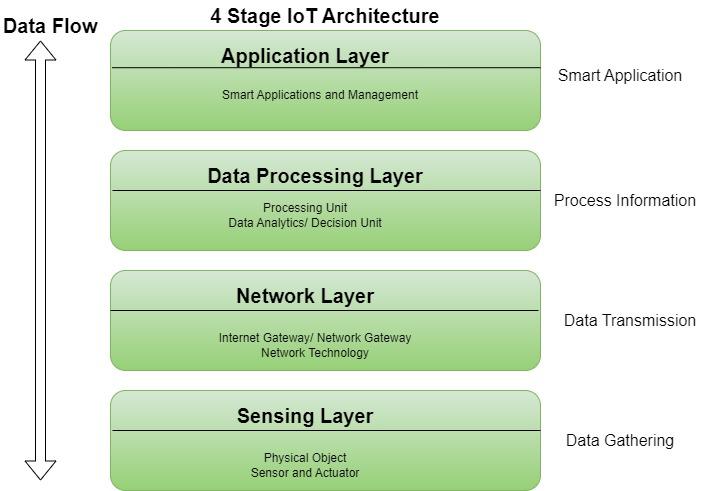
IoT devices operate by collecting, transmitting, and analyzing data to perform automated tasks or provide valuable insights. The process can be broken down into the following key steps:
Data Collection
IoT devices use built-in sensors to gather data from their surroundings. This can include:
- Environmental data: Temperature, humidity, air quality.
- Motion data: Movement, proximity, acceleration.
- Health data: Heart rate, sleep patterns, calorie intake.
For example, a smart thermostat measures room temperature and detects occupancy patterns to adjust heating or cooling accordingly.
Data Transmission
Once collected, the data is sent to cloud-based servers or local storage through communication technologies such as:
- Wi-Fi: Common in smart homes for fast and reliable connectivity.
- Bluetooth: Used for short-range communication, like wearable fitness trackers.
- Cellular networks (4G/5G): Ideal for IoT devices requiring mobility, such as smart vehicles and asset tracking systems.
Data Processing and Analysis
After transmission, the data is processed using cloud computing platforms or on-device AI algorithms. This step helps identify patterns and make automated decisions, such as:
- Sending alerts when a potential issue is detected (e.g., a smart leak detector notifying you of a water leak).
- Optimizing energy use based on historical data and user habits.
User Interaction and Automation
Finally, users can interact with IoT systems via:
- Mobile apps: Control smart home devices, view data, and set preferences.
- Voice assistants: Use voice commands to activate IoT devices (e.g., “Alexa, turn off the lights”).
- Automated responses: Devices performing tasks autonomously, like smart fridges ordering groceries when supplies are low.
IoT makes life easier by enabling devices to work together intelligently, saving time and improving efficiency.
Examples of IoT in Daily Life
IoT technology has become an essential part of everyday life, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and even safety. Here are some real-world examples of how IoT is transforming our daily routines:
1. Smart Home Devices
Smart home technology helps automate household tasks and improve comfort. Popular IoT devices include:
- Smart thermostats (e.g., Nest, Ecobee): Automatically adjust temperature based on user preferences and weather conditions, helping save energy.
- Smart lights (e.g., Philips Hue): Allow remote control, scheduling, and color adjustments via mobile apps or voice assistants.
- Smart appliances (e.g., refrigerators, ovens): Can track inventory, suggest recipes, or even start cooking with voice commands.
2. Wearable Technology
Wearables provide valuable health and fitness insights, allowing users to track their well-being effortlessly. Examples include:
- Smartwatches (e.g., Apple Watch, Fitbit): Monitor heart rate, steps, sleep patterns, and even detect irregular heart rhythms.
- Fitness trackers: Help users achieve their fitness goals by tracking workouts and providing real-time feedback.
- Smart glasses: Offer augmented reality features, enabling hands-free access to information while on the go.
3. Health and Medical Devices
IoT is revolutionizing healthcare by providing real-time monitoring and improving patient care. Examples include:
- Smart medical equipment: Devices such as connected glucose monitors and blood pressure cuffs help patients manage chronic conditions remotely.
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM): Healthcare providers can track patient vitals and provide timely interventions without in-person visits.
- Pill dispensers: Smart medication reminders ensure patients take the right dosage at the right time.
4. Smart Cities
IoT is making urban living smarter and more efficient by optimizing resources and improving public services. Examples include:
- Traffic management systems: Smart sensors and AI help control traffic lights to reduce congestion and improve travel times.
- Environmental monitoring: IoT-based air quality sensors provide real-time data to address pollution concerns.
- Smart waste management: Sensors in waste bins notify collection services when bins are full, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
From homes to cities, IoT is creating a more connected and intelligent world, simplifying daily activities and offering new possibilities for the future.
The Impact of IoT on Daily Life
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how we live, work, and interact with our surroundings. It offers numerous benefits, making life more convenient and efficient. However, it also raises concerns about privacy and security. Let’s explore the key impacts of IoT on daily life:
1. Convenience: Automating Tasks and Enhancing Lifestyle
IoT devices make life easier by automating everyday tasks and offering personalized experiences. Some examples include:
- Smart assistants: Devices like Amazon Alexa or Google Home can control multiple IoT devices with voice commands, from setting reminders to adjusting lighting.
- Automated routines: Smart homes can adjust lighting, temperature, and even security based on daily habits and preferences.
- Remote control: With IoT-enabled devices, you can monitor and control home appliances from anywhere using a smartphone app.
2. Efficiency: Energy Saving, Time Management, and Resource Optimization
IoT helps individuals and businesses save time and resources by optimizing operations. Examples include:
- Energy efficiency: Smart thermostats and lighting systems adjust usage based on occupancy, reducing energy bills.
- Time management: IoT-enabled coffee makers, smart mirrors, and other appliances can streamline morning routines.
- Supply chain optimization: Businesses use IoT to track shipments, monitor inventory, and reduce waste.
3. Security: Smart Security Systems and Privacy Considerations
While IoT enhances security with smart locks, cameras, and alarms, it also introduces risks.
- Improved security: Smart doorbells and surveillance cameras provide real-time monitoring and alerts to homeowners.
- Privacy concerns: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about how it is stored and used.
- Cybersecurity threats: Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices, potentially compromising sensitive information.
IoT is enhancing our daily lives by making tasks more manageable and optimizing resources. However, it is crucial to stay aware of potential risks and take measures to protect personal data and privacy.
Challenges of IoT
While the Internet of Things (IoT) offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges that can impact its effectiveness and security. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient use of IoT devices.
1. Data Privacy Concerns
IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal data, including location, health metrics, and usage patterns. This raises concerns about:
- Unauthorized access: Hackers could gain access to sensitive data if devices are not properly secured.
- Data misuse: Companies may collect and sell user data without clear consent, raising ethical concerns.
- Compliance issues: Many IoT devices must adhere to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to protect user privacy.
Solution: Users should regularly update their devices, use strong passwords, and review privacy policies before using IoT products.
2. Connectivity and Interoperability Issues
With so many IoT devices available, ensuring seamless communication between different brands and technologies can be challenging. Some common issues include:
- Inconsistent standards: Various devices use different communication protocols (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee), leading to compatibility problems.
- Network reliability: Poor connectivity can cause devices to malfunction or fail to sync with cloud services.
- Scalability challenges: As the number of connected devices grows, networks may struggle to handle the increased data load.
Solution: Choosing devices that follow widely accepted standards and ensuring a strong network infrastructure can improve connectivity.
3. Security Vulnerabilities and Risks
IoT devices are attractive targets for cyberattacks due to their widespread use and often weak security measures. Common risks include:
- Hacking attempts: Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities to gain control over devices, leading to data breaches or even physical harm.
- Botnet attacks: Unsecured IoT devices can be hijacked to perform large-scale attacks, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS).
- Firmware vulnerabilities: Many devices do not receive regular security updates, making them susceptible to new threats.
Solution: Implementing encryption, using firewalls, and keeping firmware updated can help mitigate security risks.
Despite these challenges, proactive measures can help users and businesses enjoy the benefits of IoT while minimizing risks.
The Future of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is continuously evolving, with exciting innovations and emerging trends shaping the way we interact with technology. As IoT becomes more advanced and widespread, it will bring even greater convenience and efficiency to our daily lives. Let’s explore what the future holds for IoT.
1. Emerging Trends in IoT
Several key advancements are driving the next generation of IoT devices and applications:
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster, more reliable connections, allowing IoT devices to operate with minimal latency and enhanced performance.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: IoT devices are becoming smarter by leveraging AI to analyze data in real time and automate decision-making processes. Discover how AI is revolutionizing the world today.
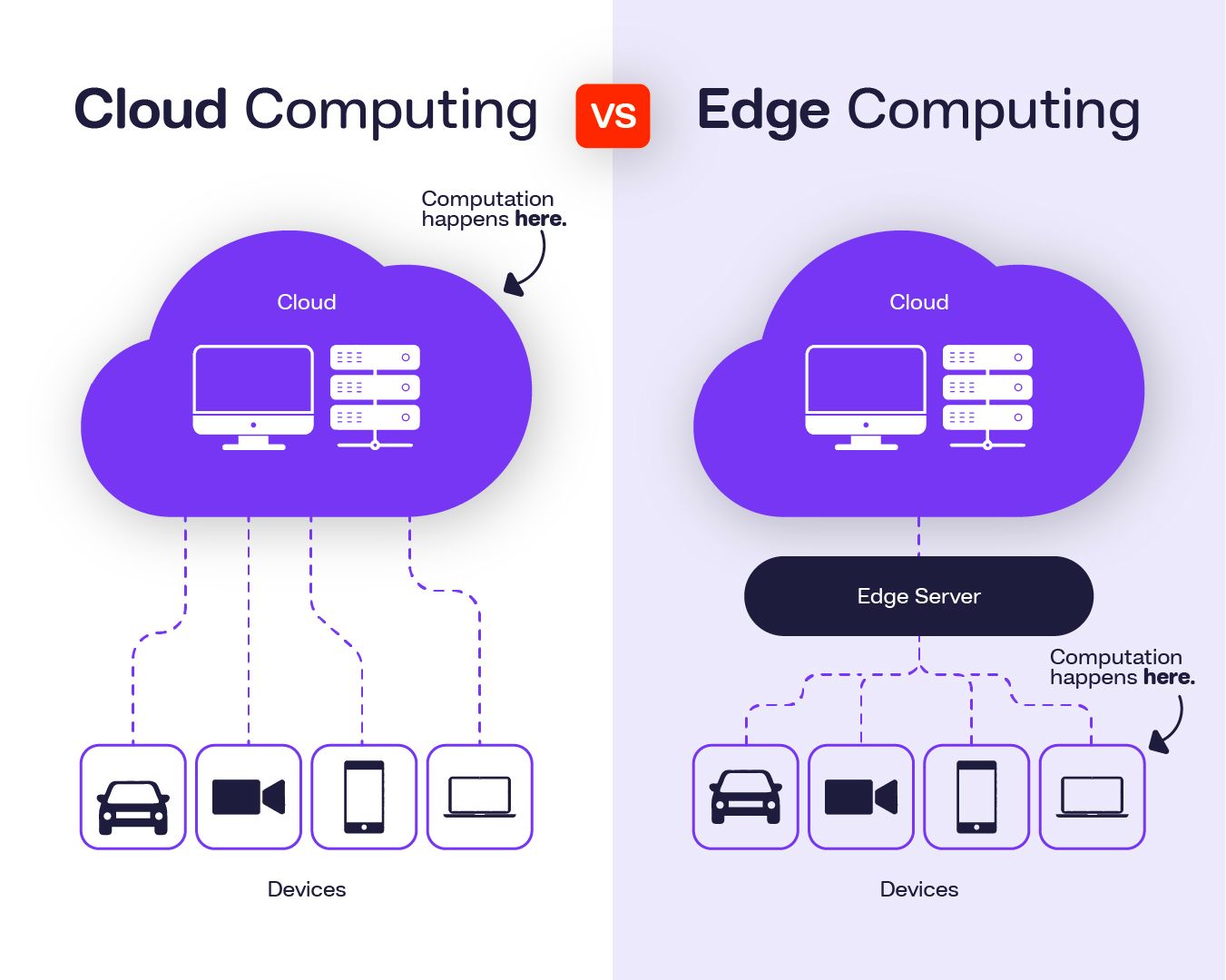
- Edge Computing: Instead of relying solely on cloud storage, IoT devices will process data locally (on the “edge”), reducing latency and improving response times for critical applications like autonomous vehicles and healthcare.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance IoT security by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof way to store data and manage transactions.
2. Potential Innovations and Their Impact on Daily Life
The future of IoT promises groundbreaking innovations across various sectors:
- Smart Homes of the Future: Advanced IoT ecosystems will enable complete automation of household tasks, from energy management to grocery shopping.
- Healthcare Revolution: IoT-powered wearable devices and remote monitoring systems will make healthcare more personalized and accessible.
- Autonomous Vehicles: IoT-enabled cars will communicate with each other and traffic systems to improve safety and optimize routes.
- Sustainable Living: IoT will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by optimizing resource consumption in smart cities and agriculture.
As IoT continues to grow, it will unlock new possibilities and create a more connected and efficient world. However, addressing security and privacy challenges will be essential to ensuring a safe and responsible adoption of these technologies.
FAQ
What is the Internet of Things (IoT) in simple terms?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to everyday objects—like home appliances, wearable devices, and vehicles connected to the internet to collect and share data. These smart devices help automate tasks, improve efficiency, and provide real-time insights to make life easier and more convenient.
How does IoT work, and what technologies does it use?
IoT works by using sensors and devices to collect data, which is then transmitted over the internet using technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. This data is processed in the cloud or locally on the device to trigger actions, such as turning off lights when no one is home or sending health alerts from wearable devices.
How will IoT evolve in the future with advancements like AI and 5G?
IoT will become smarter and faster with AI and 5G. AI will allow devices to analyze data more efficiently and make better decisions, while 5G will provide faster and more reliable connectivity, enabling seamless communication between devices in real-time. This will enhance applications like smart cities, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles.
What steps can I take to secure my IoT devices at home?
To secure your IoT devices, always use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication where possible. Keep your devices and router firmware updated to protect against security vulnerabilities. Consider setting up a separate Wi-Fi network for your IoT devices and regularly review device permissions to ensure minimal data access.
What are the biggest advantages of IoT in daily life?
IoT offers convenience, efficiency, and better resource management. It can automate routine tasks, such as adjusting home temperature or tracking fitness goals, helping you save time and energy. IoT also improves security through smart surveillance systems and enhances healthcare with remote monitoring solutions.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming everyday life by making it more connected, efficient, and convenient. From smart homes to wearable health trackers, IoT is enhancing how we live and work.
However, challenges like data privacy and security risks require attention. Staying informed and securing devices can help users fully benefit from IoT technology.
With advancements in 5G, AI, and edge computing, the future of IoT promises even smarter homes, cities, and industries.


No comment